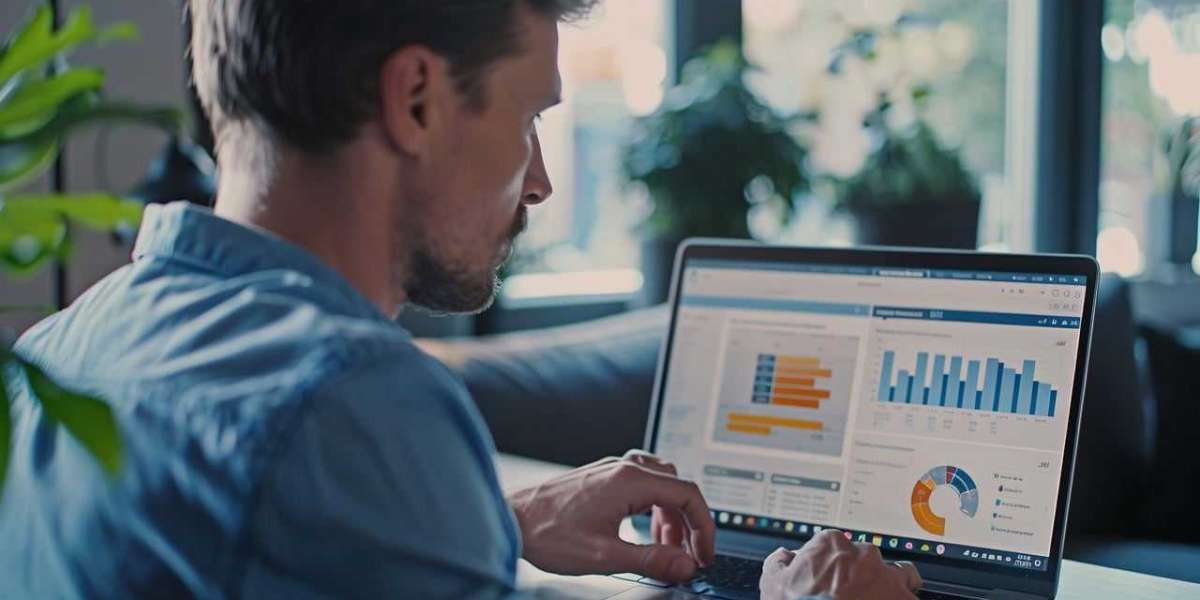
As the demand for faster, more reliable digital experiences grows, traditional content delivery networks (CDNs) are facing new challenges. Content delivery, once reliant on centralized servers, now requires innovative solutions that address the growing need for speed and low latency. This is where edge computing comes in. By bringing computing power closer to the end user, edge computing is revolutionizing how CDNs operate, offering faster content delivery, improved user experiences, and reduced strain on traditional server infrastructures. ITShark explores how edge computing is reshaping the landscape of CDNs and what this means for the future of digital content.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a decentralized computing model that processes data closer to the location where it’s generated or consumed, rather than relying on centralized data centers. In the context of content delivery, this means processing and storing data at the “edge” of the network, which is closer to the end user. This reduces the distance data has to travel, resulting in lower latency and faster access to content.
The traditional approach to CDNs involved large, centralized data centers that store and deliver content to users. While this model worked well for many years, it often created delays due to the distance between the user and the data center, particularly for users located far from these centralized locations. Edge computing addresses this problem by placing content in smaller, localized data centers, or "edge nodes," that are strategically located closer to users.
How Edge Computing Enhances CDNs
- Lower Latency and Faster Load Times
One of the primary benefits of edge computing is its ability to drastically reduce latency. By processing and storing content at the edge of the network, closer to the user, the time it takes for data to travel from the server to the user is minimized. This means that content loads faster, leading to a smoother and more responsive experience for users, whether they’re streaming videos, loading websites, or using applications.
For industries where speed is critical, such as gaming, live video streaming, or e-commerce, the reduction in latency can make a significant difference. Edge computing ensures that users in distant regions experience content delivery speeds that were once only available to those near centralized data centers.
- Bandwidth Efficiency
Edge computing helps optimize bandwidth by reducing the amount of data that needs to be sent over long distances. By processing data locally, edge nodes can handle a significant portion of content delivery without needing to send every request back to a central server. This reduces network congestion, lowers the strain on traditional servers, and ensures that bandwidth is used more efficiently, particularly during peak usage times.
This efficiency also translates into cost savings. Traditional CDNs require significant infrastructure investments to manage large data centers and bandwidth costs. With edge computing, companies can deploy smaller, more localized servers, leading to more cost-effective content delivery models.
- Scalability and Flexibility
As digital content consumption grows, scalability becomes a key concern for CDNs. Edge computing allows for greater scalability by enabling content to be distributed across a large number of edge nodes. Each node can handle local traffic, reducing the need for centralized resources to scale up to accommodate demand. This distributed approach allows CDNs to efficiently manage traffic spikes and handle large-scale events, such as product launches or viral content.
Additionally, edge computing is more adaptable to specific user needs. By leveraging localized data centers, content can be tailored based on geographic or demographic factors, ensuring that users receive the most relevant and optimized content.
- Improved Reliability and Redundancy
Edge computing enhances the reliability of CDNs by providing redundancy through the use of multiple edge nodes. If one edge node fails, traffic can be rerouted to nearby nodes, minimizing downtime and ensuring that content remains accessible. This redundancy is crucial for businesses that rely on constant uptime, such as streaming services, online retailers, and cloud-based platforms.
By decentralizing content delivery, edge computing reduces the risk of a single point of failure, improving the overall resilience of the network. This ensures that users experience minimal disruption, even in the event of technical issues or hardware failures.
- Better Data Security and Privacy
Edge computing also plays a role in improving data security and privacy. By processing sensitive data locally at the edge, businesses can reduce the amount of personal data sent to central servers, minimizing the potential exposure of private information. This is particularly important as privacy regulations, such as GDPR, become more stringent.
Edge computing enables companies to store and process data in specific geographic regions, ensuring compliance with local data protection laws. This localized approach enhances data security while still providing users with fast and efficient content delivery.
The Future of CDNs with Edge Computing
As edge computing continues to evolve, its impact on CDNs will only grow. With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous vehicles, and other data-intensive technologies, the need for faster, more efficient content delivery will become even more critical. Edge computing is already positioning itself as a key enabler of these next-generation digital experiences.
For ITShark and other tech-forward companies, embracing edge computing in CDN strategies means providing clients with faster, more reliable, and scalable content delivery solutions. By integrating edge nodes into their CDN infrastructure, businesses can meet the demands of today’s digital landscape while preparing for the future of connectivity.
Conclusion
Edge computing is transforming the way content is delivered across the internet. By decentralizing content delivery and processing data closer to users, edge computing reduces latency, optimizes bandwidth, improves scalability, and enhances reliability and security. As businesses continue to adopt this technology, the role of traditional CDNs will be reshaped, creating faster, more efficient, and more personalized digital experiences. The integration of edge computing into CDN strategies is a critical step in meeting the ever-growing demand for seamless, high-performance content delivery, and it’s clear that the future of the internet is on the edge.
 Meet Ups
Meet Ups
 Experiences
Experiences
 Learning Center
Learning Center
 Accommodation
Accommodation
 Roomie
Roomie
 Ride
Ride
 Spread the Word
Spread the Word
 Student Bazaar
Student Bazaar
 Jobs
Jobs
 Blogs
Blogs
 About StudentInsta
About StudentInsta

